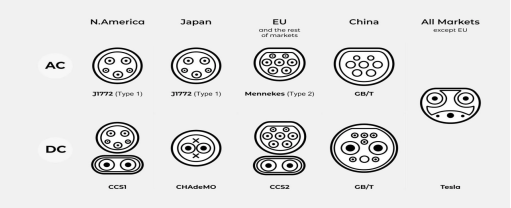
Combo sockets can allow slow charging and fast charging of electric vehicles. It is the most widely used socket type in Europe, including Audi, BMW, Chrysler, Daimler, Ford, General Motors, Porsche and Volkswagen, all equipped with SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) ) charging interface developed.
On October 2, 2012, the SAE J1772 revised draft voted by SAE relevant committee members became the only official DC charging standard in the world. The launch of this standard is to change the current situation of a mixed charging system and increase consumers' enthusiasm for purchasing electric vehicles. The core of the DC fast charging standard based on the revised version of J1772 is the Combo Connector.
The previous version of the standard (developed in 2010) specified the specifications of the basic J1772 connector for AC charging, with lower charging levels (AC Level 1 for 120V, Level 2 for 240V). This basic connector is widely used today and is compatible with Nissan Leaf, Chevrolet Volt and Mitsubishi i-MiEV electric vehicles. In addition to all the original functions, the Combo Connector in the new version of the J1772 standard formulated in 2012 also has two more pins, which can be used for DC fast charging, but it is not compatible with older electric vehicles currently produced.
The fast charging method used by CHAdeMO is as shown in the figure, and the current is controlled by the car's CAN bus signal. That is, while monitoring the battery status, it calculates the current value required for charging in real time and sends a notification to the charger through the communication line; the fast charger receives the current command from the car in time and provides the current according to the specified value.
The battery management system monitors the battery condition and controls the current in real time, fully realizing all the functions required for fast and safe charging, ensuring that charging is not limited by battery versatility. In Japan, 1,154 fast chargers installed in accordance with CHAdeMO standards are in use. In the United States, CHAdeMO charging stations have also been widely "cast". The latest data from the U.S. Department of Energy shows that there are 1,344 CHAdeMO AC fast charging stations in the United States.
Advantages: In addition to the data control line, CHAdeMO also uses the CAN bus as the communication interface. Due to its superior noise immunity and high error detection capability, CHAdeMO has high communication stability and reliability. Its good charging safety record has been recognized by the industry.
Electric vehicle models that support this charging standard include: Nissan Leaf, Mitsubishi Outlander plug-in hybrid, Citroen C-ZERO, Peugeot iON, Citroen Berlingo, Peugeot Partner, Mitsubishi i-MiEV, Mitsubishi MINICAB-MiEV, Mitsubishi MINICAB-MiEV truck , Honda Fit electric version, Mazda DEMIO EV, Subaru Stella plug-in hybrid, Nissan eEV200, etc. It should be noted here that both Nissan Leaf and Mitsubishi i-MiEV electric vehicles have two different charging sockets. One of them is suitable for the basic J1772 connector, which is the Combo connector introduced in the first part; the other is suitable for Japanese native CHAdeMO standard connector.
Tesla cars have their own charging standard and claim to be able to fully charge their batteries in 30 minutes and run more than 300 kilometers. Therefore, its charging socket has a maximum capacity of 120kw and a maximum current of 80A.
Currently, Tesla has 908 Supercharging stations in the United States. In order to enter China, Tesla has also established 7 super charging stations in my country, 3 in Shanghai, 2 in Beijing, 1 in Hangzhou, and 1 in Shenzhen. In addition, in order to better integrate into various regions, Tesla plans to give up control of charging standards and adopt the national standards of each country. It has already done so in China.
China issued GB/T 20234-2006 "General Requirements for Plugs, Sockets, Vehicle Couplers and Vehicle Jacks for Conductive Charging of Electric Vehicles" in 2006. This national standard specifies in detail the charging currents of 16A, 32A, 250A AC and The connection classification method of 400A DC mainly draws on the standard proposed by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) in 2003, but this standard does not specify the number of connection pins, physical size and interface definition of the charging interface. In 2011, the recommended standard GB/T 20234-2011 was launched, replacing part of the content in GB/T 20234-2006. The latest standard is GB/T 20234-2015. The standard stipulates that the AC rated voltage does not exceed 690V and the frequency is 50Hz. , the rated current does not exceed 250A; the DC rated voltage does not exceed 1000V, and the rated current does not exceed 400A.